Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a critical medical emergency where the heart abruptly stops
beating due to an electrical malfunction, leading to the cessation of blood flow to the brain and
other vital organs. Immediate treatment such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and
defibrillation is essential to survival, as death can occur within minutes without intervention.
Understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and being prepared to act with CPR and
an AED are essential steps in saving lives
WHAT IS SUDDEN CARDIAC ARREST?
Sudden cardiac arrest is caused by an electrical disturbance that disrupts the heart's rhythm,
making it unable to pump blood effectively. This differs from a heart attack, which is caused by
blocked blood flow to the heart; however, a heart attack can sometimes trigger sudden cardiac
arrest. During SCA, the person loses consciousness quickly and stops breathing.
SYMPTOMS AND WARNING SIGNS
SCA usually occurs without warning and symptoms are immediate, including sudden collapse,
absence of pulse, and loss of consciousness. In some cases, people may experience warning
signs like chest discomfort, palpitations, shortness of breath, and weakness before the event,
though often there are no preceding symptoms.
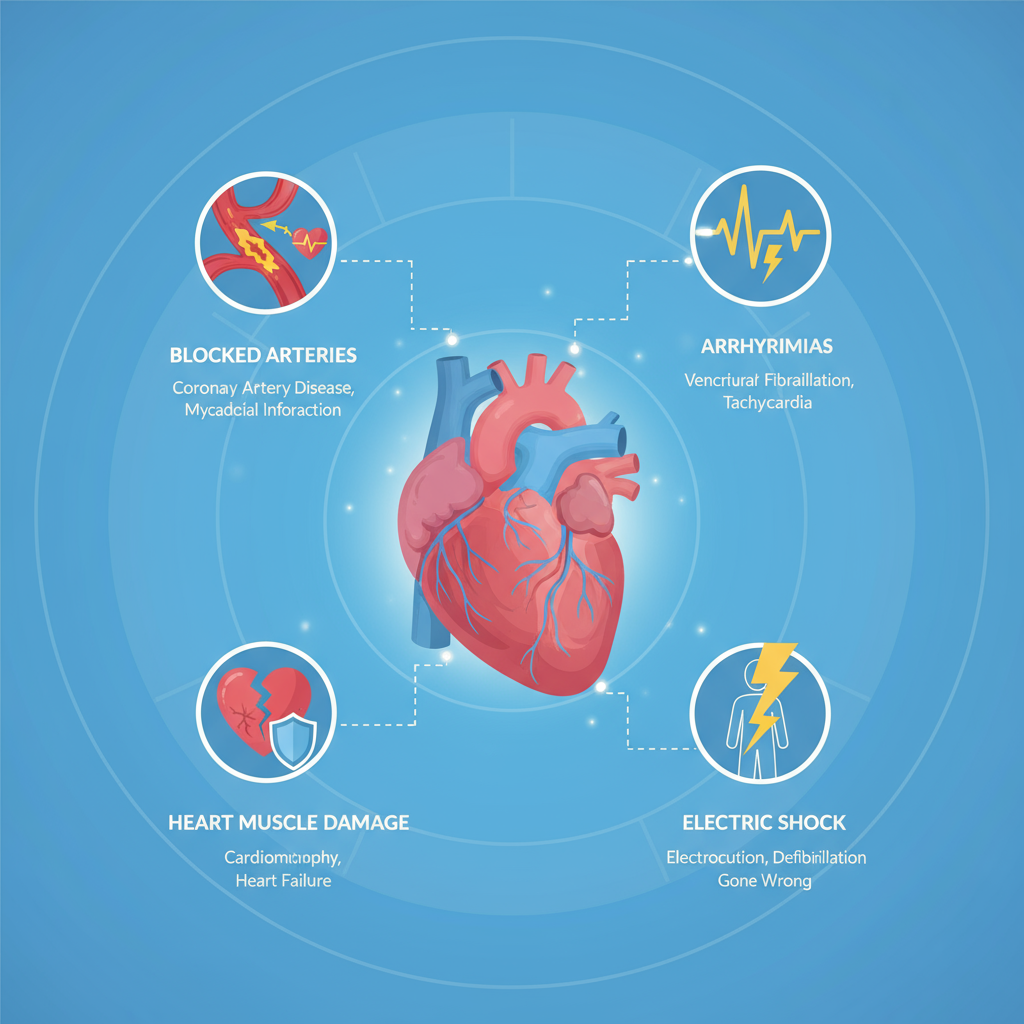
CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS
The primary cause of SCA is abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias), especially ventricular
fibrillation, which causes the heart’s lower chambers to quiver instead of pumping blood.
Underlying causes include heart disease, structural heart defects, certain inherited conditions
like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and other factors such as a sudden blow to the chest or
severe allergic reactions.


Jilly Smith 29 Oct 2022
Nulla sed viveraut lorem tetur diam nunc bibendum imperdiets ipsum dolor tur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt labore.
Jilly Smith 29 Oct 2022
Nulla sed viveraut lorem tetur diam nunc bibendum imperdiets ipsum dolor tur adipisicing elit, sed do .